Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA) Hair Loss — Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
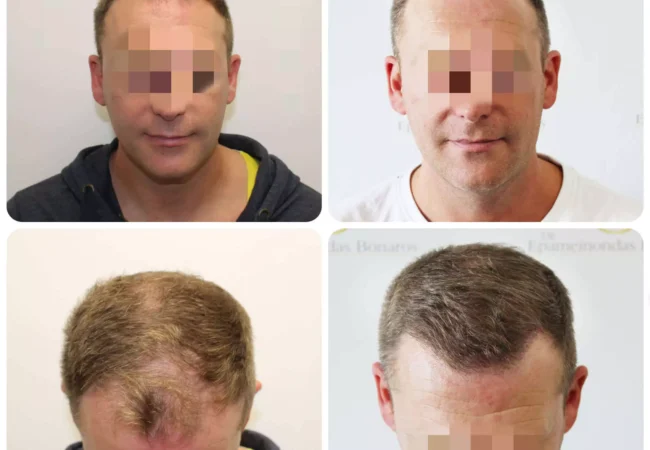
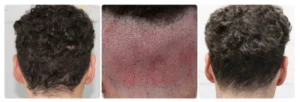
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA) Hair Loss — Causes, Symptoms & Treatments DUPA (Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia) is a relatively uncommon type of hair loss that does not follow a specific pattern. DUPA hair loss causes overall thinning, resulting in a loss of hair density and coverage. Continue reading this article to